| Phone |
| |
| |
| 대표전화 |
1577-7956 |
| 본 사 |
031-457-9187 |
| 대 전 |
042-932-1265 |
| |
|
| Web Site Visitors |
| |
| |
| Today |
1281 |
| Yesterday |
1049 |
| Since 2006 |
2,410,163 |
| |
|
 |
|
| 영진코퍼레이션 종합카다로그 |
|
|
| ■ |
Biomolecular Binding Kinetics on the Octet® Platform |
|
|
- Renee Tobias, Sriram Kumaraswamy, David Apiyo, Sartorius, Fremont, CA |
| Abstract |
| |
바이오 의약품 개발과정에서 생체분자의 상호 반응을 확인하고 정량화 하는 것은 매우 중요합니다.
Octet® system 은 labeling 을 사용하지 않고 Protein-Protein, Antigen-Antibody, Drug-Receptor 결합과 같은 생체 내 결합 반응을
Bio-layer interferometry (BLI) 방법을 통해 매우 신속하고 정밀하게, 실시간으로 측정이 가능합니다.
또한, 기존의 실험법으로 측정하기 불편했던 결합 특이성, 친화도와 분자간 상호반응에 대한 역학을 간편하게 확인하고 정량화 할 수 있습니다. |
|
 |
| |
| Octet® system 은 바이오 의약품 개발 과정의 기초 연구 단계에서 수행하는 수 많은 분석 실험에서 연구자를 도와 매우 신속하고
정밀하게 최상의 결과를 얻을 수 있는 최선의 방법이 될 수 있습니다. |
| Bio-Layer Interferometry (BLI) |
| |
|
BLI 는 Interferometry (간섭 측정법) 의 원리를 이용하여 생체 분자의 상호 반응을 실시간으로 측정하는 기술입니다.
간섭 측정법은 하나의 광원에서 출발한 빛을 두 갈래 이상으로 나누어 진행 경로에 차이가 생기도록 한 후, 빛이 다시 만났을 때 일어나는
간섭 현상을 이용한 측정 방법입니다. Octet® System 은 간섭 측정법의 원리를 응용하여 생체 분자 사이의 상호작용을 측정하고 분석합니다. BLI 의 개념은 다음과 같습니다. |
| |
Biosensor 의 tip 에는 생체 분자(Protein, Antibody) 가 붙을 수 있는 층과 그 안쪽 부분에 광학 층, 두 개의 층으로 이루어져 있습니다 (Figure 1).
이 biosensor tip 에 백색광을 조사하면 그 빛은 이 두개의 층에서 각각 반사가 일어납니다.
각 층에서 반사된 두 개의 반사광은 간섭이 발생해 반사광의 진폭이 증가되거나 감소하게 됩니다. 이때 발생한 간섭 패턴을 CCD array detector 가 감지하게 됩니다. |
|
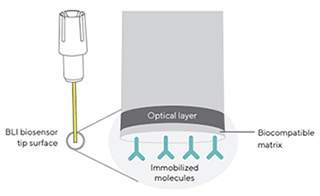
Figure 1 : A Dip and Read biosensor, illustrating the two optical interfaces
at the biosensor tip: the internal reference layer (optical layer) and the
surface biocompatible matrix on which ligand molecules are immobilized |
| |
Biosensor 의 tip 을 sample 이 들어 있는 microplate 의 well 에 넣어주면 측정하고자 하는 분자들은 생체 분자가 붙은 층에 결합하게 되고,
점점 더 많은 분자들이 결합하여 대상 분자들이 하나의 층을 이루게 됩니다.
그 결과 생체 분자 층의 두께가 두꺼워져 광원으로부터 생체 분자 층 사이의 거리가 변하게 됩니다.
그 결과 생체 분자 층에서 반사된 반사광의 이동 거리가 변하며 광학 층과의 간섭 패턴의 위상 변화가 발생합니다.
이러한 위상 변화를 CCD array detector 가 측정하게 됩니다.
이 과정은 실시간으로 이루어져 생체 분자 결합의 역학적 데이터도 함께 얻을 수 있습니다 (Figure 2). |
|
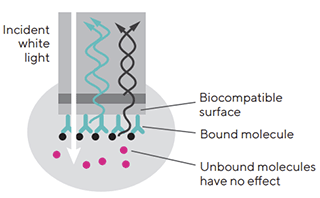
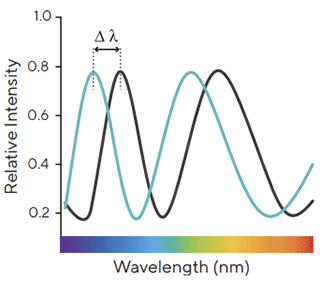 Figure 2 : interference pattern of white light reflected from two surfaces. Changes
in the number of molecules bound to the biosensor causes a shift in the interference pattern that is measured in real time
Figure 2 : interference pattern of white light reflected from two surfaces. Changes
in the number of molecules bound to the biosensor causes a shift in the interference pattern that is measured in real time |
| Advantages of Label-free Analysis |
| |
Kinetic analysis 는 가역적인 비공유결합에서 상호작용 친화성과 생체 분자의 결합 및 해리 속도를 측정하는 과정입니다.
상호반응하는 물질 중 하나는 Octet® 의 biosensor 표면에 고정되고 다른 하나는 sample 용액에 buffer 와 함께 plate 에 둡니다. Assay 는 다음과 같은 단계로 이루어집니다 (Figure 3).
① Baseline : Assay buffer 를 이용한 기준 값을 설정해 줍니다.
② Loading : Antibody 와 같은 생체 분자를 biosensor 의 표면에 고정시켜 줍니다.
③ Baseline : Biosensor 를 buffer solution 에 넣어 생체 분자가 표면에 완전히 loading 되도록 해줍니다.
④ Association : Antibody 가 표면에 붙어 있는 biosensor 를 테스트할 시료가 있는 solution 에 넣어 실험하고자 하는 생체 분자와 표면의 생체 분자 사이에 결합을 유도합니다.
⑤ Dissociation : Biosensor 를 시료가 없는 solution 으로 옮겨 상호작용한 두 분자의 해리를 유도합니다.
위의 과정을 실험하고자 하는 시료의 농도가 다른 몇가지 용액에서 (최대 8개) 동시에 시행하여 결과값을 비교 분석할 수 있습니다. |
| |
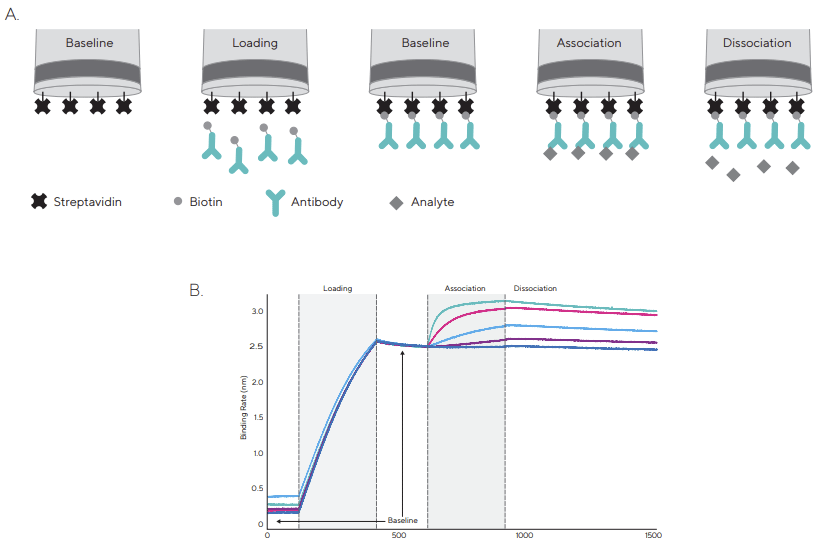
Figure 3 : A typical binding kinetics experiment using Streptavidin Biosensors.
A) After an initial baseline step in buffer, biosensors are dipped into solution with biotinylated ligand. In this example, ligand molecule is an antibody.
A second baseline step is performed followed by association and dissociation of analyte molecule in solution.
B) A raw data sensorgram showing real-time data acquisition for each step of a kinetic assay |
| Binding Kinetics - Basic Principles |
| |
Octet® system 을 통해 얻을 수 있는 kinetic characterization 정보는 분자간 상호작용을 설명하는데 부족함이 있는 ELISA 와 같은 기존의 실험법을 보완할 수 있습니다.
Octet® system 은 생체 분자의 결합 과정의 역학, 친화도 그리고 활성을 실시간으로 매우 정밀하게 보여주기 때문입니다.
Figure 4 에서 A, B 두 sample 의 affinity constant (KD) 는 비슷하게 보이지만 sample A 의 on-rate and off-rate 는
sample B 에 비해 느린 결합력을 보이고 있다는 것을 알 수 있는데, 이러한 데이터는 ELISA 와 같은 기존 분석 방법으로는 확인할 수 없습니다.
Octet® System 은 생체 분자간 결합을 실시간으로 측정 함으로써 생체 분자간 결합 친화도에 대한 더 높은 수준의 정량화 된 정보를 연구자에게 제공합니다. |
| |
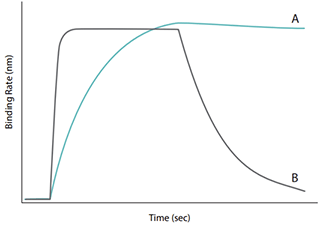
Figure 4 : Sensorgram traces from two interactions having similar
affinity constants but different binding profiles |
|







